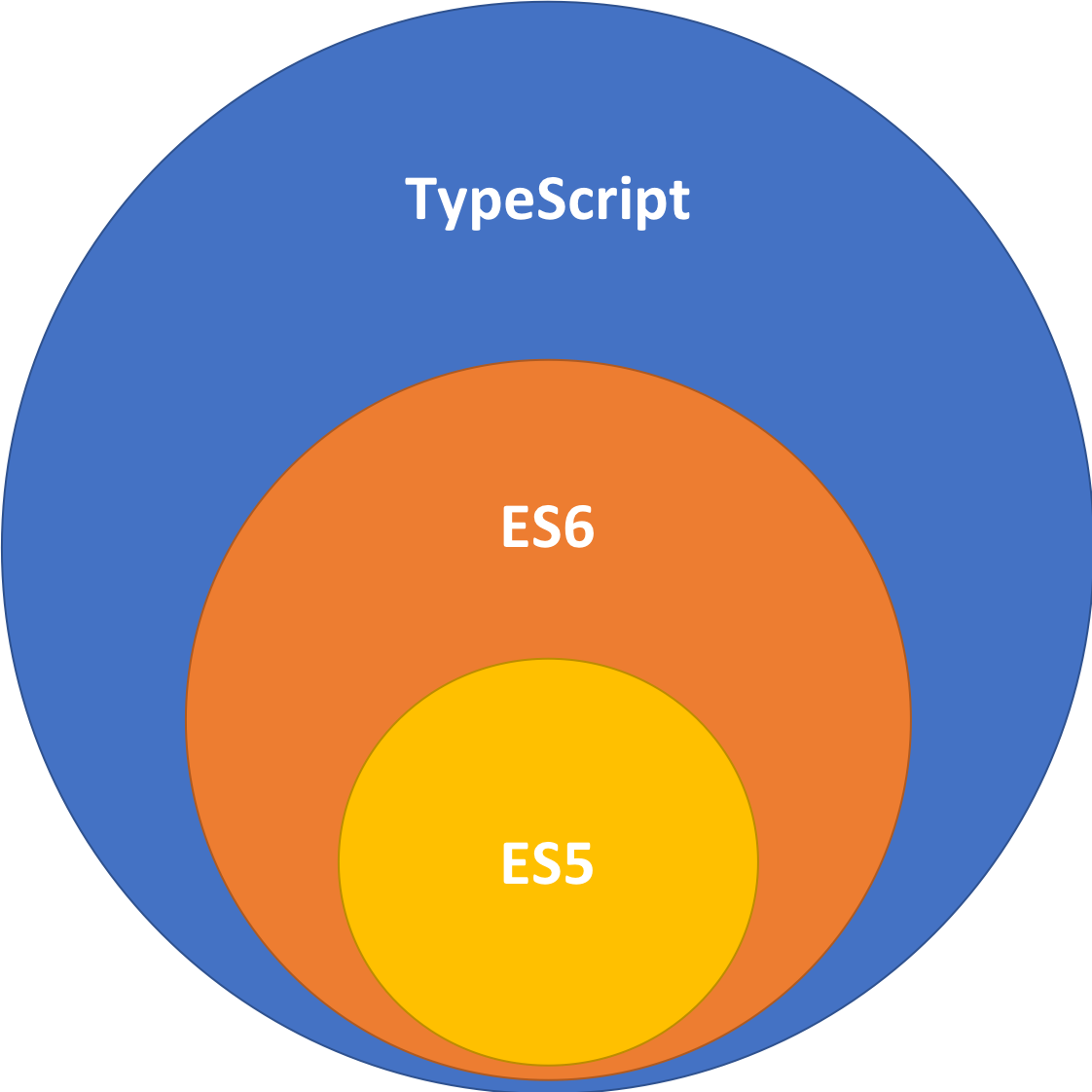
ES5 핵심 정리
연구개발본부
2018. 3. 17.
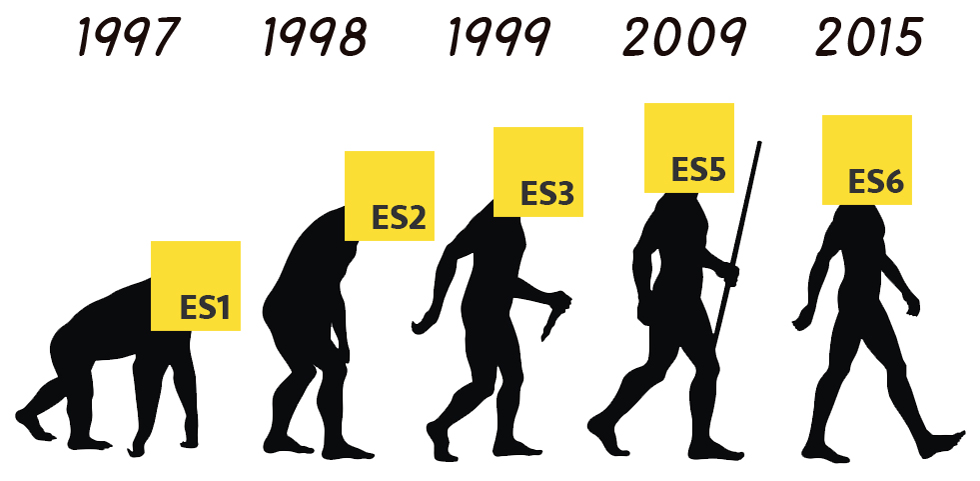
History
- ES1 : 1997
- ES2 : 1998
- ES3 : 1999
- ES5 : 2009
- ES6 : 2015 (ES2015)
- ES2016
Getter accessors
var obj = {
get x(){
return 1;
}
}
console.log(obj.x); // 1
| IE8 | IE9 | IE10 | IE11 | chrome | firefox | safari |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Setter accessors
var value = 0;
var obj = {
set x(v) {
value = v;
}
}
obj.x = 2;
console.log(value); // 2
| IE8 | IE9 | IE10 | IE11 | chrome | firefox | safari |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Trailing commas in Object literals
var obj = {
a: true,
b: false, // ok
}
console.log(obj.b); // false
| IE8 | IE9 | IE10 | IE11 | chrome | firefox | safari |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Trailing commas in array literals
var arr = [1, 2, ];
console.log(arr.length); // 2
| IE8 | IE9 | IE10 | IE11 | chrome | firefox | safari |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Reserved words as property names
var obj = {
if: 1,
else: 2,
catch: 3
}
console.log(obj.if); // 1
console.log(obj.else); // 2
console.log(obj.catch); // 3
| IE8 | IE9 | IE10 | IE11 | chrome | firefox | safari |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Object.create
create a new object, using an existing object to provide the newly created object’s __proto__
var person = {
isHuman: false,
print: function () { console.log(this.name + ", " + this.isHuman);}
};
var me = Object.create(person);
me.name = "Matthew";
me.isHuman = true; // can be overwritten
me.print(); // Matthew, true
console.log(me.__proto__ == person) // true
console.log(JSON.stringify(me)); //{"name":"Matthew","isHuman":true}
console.log(JSON.stringify(person));//{"isHuman":false}
| IE8 | IE9 | IE10 | IE11 | chrome | firefox | safari |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Object.defineProperty
defines a new property directly on an object, or modifies an existing property on an object, and returns the object.
var object1 = {};
Object.defineProperty(object1, 'property1', {
value: 42,
writable: false
});
object1.property1 = 77;
// throws an error in strict mode
console.log(object1.property1); // 42
| IE8 | IE9 | IE10 | IE11 | chrome | firefox | safari |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Object.defineProperties
defines new or modifies existing properties directly on an object, returning the object.
var o1 = {};
Object.defineProperties(o1, {
prop1: { value: 42, writable: true},
prop2: {}
});
console.log(o1.prop1); // 42
| IE8 | IE9 | IE10 | IE11 | chrome | firefox | safari |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Object.getPrototypeOf
returns the prototype (i.e. the value of the internal [[Prototype]] property) of the specified object.
var prototype1 = {};
var object1 = Object.create(prototype1);
var object2 = Object.getPrototypeOf(object1)
console.log(object2 === prototype1); //true
console.log(object2 === object1.__proto__); //true
| IE8 | IE9 | IE10 | IE11 | chrome | firefox | safari |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Object.keys
returns an array of a given object’s own enumerable properties, in the same order as that provided by a for…in loop
var arr = ['a', 'b', 'c']; // simple array
console.log(Object.keys(arr)); // ['0', '1', '2']
var obj = { 0: 'a', 1: 'b' }; // array like object
console.log(Object.keys(obj)); // ['0', '1' ]
// array like object with random key ordering
var anObj = { 100: 'a', 2: 'b', 7: 'c' };
console.log(Object.keys(anObj)); // ['2', '7', '100']
| IE8 | IE9 | IE10 | IE11 | chrome | firefox | safari |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Object.seal
객체를 밀봉한다. 객체를 밀봉하면 그 객체에는 새로운 속성을 추가할 수 없고, 현재 존재하는 모든 속성을 설정 불가능 상태로 만들어 준다. 하지만 쓰기 가능한 속성의 값은 밀봉 후에도 변경할 수 있다. (Object.freeze()와의 차이)
var o1 = { prop1: 42 };
var o2 = Object.seal(o1);
console.log(o1 === o2); // true
console.log(o1.prop1 + " " + o2.prop1); // 42 42
o1.prop1 = 33;
console.log(o1.prop1 + " " + o2.prop1); // 33 33
delete o1.prop1; // cannot delete
console.log(o1.prop1 + " " + o2.prop1); // 33 33
| IE8 | IE9 | IE10 | IE11 | chrome | firefox | safari |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Object.freeze
불변(immutable) 객체를 만든다. 객체에 새로운 속성(property)를 추가할 수 없고, 객체에 원래 존재하던 속성을 제거할 수 없으며, 객체의 속성, 열거가능성(enumerability), 설정가능성(configurability), 값 쓰기 가능성(writability)을 변경할 수 없게 만든다는 것을 의미한다.
var o1 = { prop1: 42 };
var o2 = Object.freeze(o1);
console.log(o1 === o2); // true
console.log(o1.prop1 + " " + o2.prop1); // 42 42
o1.prop1 = 33; // error in strict mode
console.log(o1.prop1 + " " + o2.prop1); // 42 42
delete o1.prop1; // cannot delete
console.log(o1.prop1 + " " + o2.prop1); // 42 42
| IE8 | IE9 | IE10 | IE11 | chrome | firefox | safari |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Object.preventExtensions
prevents new properties from ever being added to an object
var o1 = {};
Object.preventExtensions(o1);
try {
Object.defineProperty(o1, 'prop1', {value: 42});
} catch (e) {
console.log(e);
//TypeError: Cannot define property prop1,
// object is not extensible
}
| IE8 | IE9 | IE10 | IE11 | chrome | firefox | safari |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Object.isSealed
determines if an object is sealed.
var o1 = { prop1: 42 }
console.log(Object.isSealed(o1)); // false
Object.seal(o1);
console.log(Object.isSealed(o1)); // true
| IE8 | IE9 | IE10 | IE11 | chrome | firefox | safari |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Object.isFrozen
determines if an object is frozen.
var o1 = { prop1: 42 }
console.log(Object.isFrozen(o1)); // false
Object.freeze(o1);
console.log(Object.isFrozen(o1)); // true
| IE8 | IE9 | IE10 | IE11 | chrome | firefox | safari |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Object.isExtensible
determines if an object is extensible (whether it can have new properties added to it).
var o1 = { prop1: 42 }
console.log(Object.isExtensible(o1)); // ture
Object.preventExtensions(o1);
console.log(Object.isExtensible(o1)); // false
| IE8 | IE9 | IE10 | IE11 | chrome | firefox | safari |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptor
returns a property descriptor for an own property (not in the object’s prototype chain).
var obj1 = { prop1: 42 }
var desc1 = Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptor(obj1, 'prop1');
console.log(desc1.configurable); // true
console.log(desc1.value); // 42
| IE8 | IE9 | IE10 | IE11 | chrome | firefox | safari |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
[fit]Object.getOwnPropertyNames
returns an array of all properties (including non-enumerable properties except for those which use Symbol) found directly upon a given object.
var o1 = { a: 1, b: 2, c: 3 };
console.log(Object.getOwnPropertyNames(o1));
// ["a", "b", "c"]
| IE8 | IE9 | IE10 | IE11 | chrome | firefox | safari |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Array.isArray
determines whether the passed value is an Array.
console.log(Array.isArray([1, 2, 3])); // true
console.log(Array.isArray({foo: 123})); // false
console.log(Array.isArray('foobar')); // false
console.log(Array.isArray(undefined)); // false
| IE8 | IE9 | IE10 | IE11 | chrome | firefox | safari |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Array.prototype.indexOf
returns the first index at which a given element can be found in the array, or -1 if it is not present.
var beasts = ['ant', 'bison', 'camel', 'duck', 'bison'];
console.log(beasts.indexOf('bison')); // 1
// start from index 2
console.log(beasts.indexOf('bison', 2)); // 4
console.log(beasts.indexOf('giraffe')); // -1
| IE8 | IE9 | IE10 | IE11 | chrome | firefox | safari |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Array.prototype.lastIndexOf
returns the last index at which a given element can be found in the array, or -1 if it is not present. The array is searched backwards, starting at fromIndex.
var beasts = ['ant', 'bison', 'camel', 'duck', 'bison'];
console.log(beasts.lastIndexOf('bison')); // 4
// start from index 2
console.log(beasts.lastIndexOf('bison', 2)); // 1
console.log(beasts.lastIndexOf('giraffe')); // -1
| IE8 | IE9 | IE10 | IE11 | chrome | firefox | safari |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Array.prototype.every
tests whether all elements in the array pass the test implemented by the provided function.
function isBelow1(v) { return v < 40; }
function isBelow2(v) { return v < 20; }
function isBelow3(v) { return v < 0; }
var a1 = [1, 30, 39, 29, 10, 13];
console.log(a1.every(isBelow1)); // true
console.log(a1.every(isBelow2)); // false
console.log(a1.every(isBelow3)); // false
| IE8 | IE9 | IE10 | IE11 | chrome | firefox | safari |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Array.prototype.some
tests whether at least one element in the array passes the test implemented by the provided function.
function isBelow1(v) { return v < 40; }
function isBelow2(v) { return v < 20; }
function isBelow3(v) { return v < 0; }
var a1 = [1, 30, 39, 29, 10, 13];
console.log(a1.some(isBelow1)); // true
console.log(a1.some(isBelow2)); // true
console.log(a1.some(isBelow3)); // false
| IE8 | IE9 | IE10 | IE11 | chrome | firefox | safari |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Array.prototype.forEach
executes a provided function once for each array element.
var array1 = ['a', 'b', 'c'];
array1.forEach(function(element) {
console.log(element);
});
// a
// b
// c
| IE8 | IE9 | IE10 | IE11 | chrome | firefox | safari |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Array.prototype.map
creates a new array with the results of calling a provided function on every element in the calling array.
var array1 = [1, 4, 9, 16];
var map1 = array1.map(function(x) { return x * 2; });
console.log(map1); // [2, 8, 18, 32]
var map2 = array1.map(x => x * 2);
console.log(map2); // [2, 8, 18, 32]
| IE8 | IE9 | IE10 | IE11 | chrome | firefox | safari |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Array.prototype.filter
creates a new array with all elements that pass the test implemented by the provided function
var w1 = ['spray', 'destruction', 'present'];
var r1 = w1.filter(function(w) { return w.length > 6; });
console.log(r1); // ["destruction", "present"]
var r2 = w1.filter(w => w.length > 6);
console.log(r2); // ["destruction", "present"]
| IE8 | IE9 | IE10 | IE11 | chrome | firefox | safari |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Array.prototype.reduce
applies a function against an accumulator and each element in the array (from left to right) to reduce it to a single value.
arr.reduce(callback[, initialValue]) callback(prev, curr, idx, arr)
var array1 = ['B', 'C', 'D'];
var reducer = (sum, curr) => sum + curr;
console.log(array1.reduce(reducer)); // BCD
console.log(array1.reduce(reducer, 'A')); // ABCD
| IE8 | IE9 | IE10 | IE11 | chrome | firefox | safari |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Array.prototype.reduceRight
applies a function against an accumulator and each value of the array (from right to left)to reduce it to a single value.
arr.reduceRight(callback[, initialValue]) callback(prev, curr, idx, arr)
var array1 = ['A', 'B', 'C'];
var reducer = (sum, curr) => sum + curr;
console.log(array1.reduceRight(reducer)); // CBA
console.log(array1.reduceRight(reducer, 'D')); // DCBA
| IE8 | IE9 | IE10 | IE11 | chrome | firefox | safari |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Array.prototype.sort
compareFn must be function or undefined
console.log([1,2].sort(undefined)); // [1,2]
console.log([1,2].sort((a,b) => a<b)); // [2,1]
// TypeError: The comparison function must be either
// a function or undefined
try { [1,2].sort(null); } catch (e) {console.log(e)}
try { [1,2].sort(true); } catch (e) {console.log(e)}
try { [1,2].sort({ }); } catch (e) {console.log(e)}
try { [1,2].sort(/a/g); } catch (e) {console.log(e)}
| IE8 | IE9 | IE10 | IE11 | chrome | firefox | safari |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Property access on strings
There are two ways to access an individual character in a string.
- str.charAt()
- str.[number]
console.log('cat'.charAt(1)); // 'a'
console.log('cat'[1]); // 'a'
| IE8 | IE9 | IE10 | IE11 | chrome | firefox | safari |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
String.prototype.trim
removes whitespace from both ends of a string.
- whiepace
- character : space, tab, no-break space, etc.
- line terminator : LF, CR, etc
var orig = ' foo ';
console.log(orig.trim()); // 'foo'
var orig = 'foo ';
console.log(orig.trim()); // 'foo'
| IE8 | IE9 | IE10 | IE11 | chrome | firefox | safari |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Date.prototype.toISOString
ISO 8601 format.(YYYY-MM-DDTHH:mm:ss.sssZ or ±YYYYYY-MM-DDTHH:mm:ss.sssZ)
var d1 = new Date('05 October 2011 14:48 UTC');
console.log(d1.toString()); // Wed Oct 05 2011 23:48:00 GMT+0900 (KST)
console.log(d1.toISOString()); // 2011-10-05T14:48:00.000Z
d1.setFullYear(200100);
console.log(d1.toString()); // Wed Oct 05 200100 23:48:00 GMT+0900 (KST)
console.log(d1.toISOString()); // +200100-10-05T14:48:00.000Z
d1.setFullYear(-100);
console.log(d1.toString()); // Wed Oct 05 -100 23:48:00 GMT+0900 (KST)
console.log(d1.toISOString()); // -000100-10-05T14:48:00.000Z
| IE8 | IE9 | IE10 | IE11 | chrome | firefox | safari |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Date.now
returns the number of milliseconds elapsed since January 1, 1970 00:00:00 UTC.
var start = Date.now();
console.log("starting timer...");
setTimeout(function() {
var millis = Date.now() - start;
console.log("elapsed = " + Math.floor(millis/1000)); // 2
}, 2000);
| IE8 | IE9 | IE10 | IE11 | chrome | firefox | safari |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Date.prototype.toJSON
returns a string representation of the Date object.
var ev = new Date('August 19, 1975 23:15:30 UTC');
var d = event.toJSON();
console.log(d); // 1975-08-19T23:15:30.000Z
console.log(new Date(d).toUTCString());
// Tue, 19 Aug 1975 23:15:30 GMT
| IE8 | IE9 | IE10 | IE11 | chrome | firefox | safari |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Function.prototype.bind
첫번째 인자로 this 객체를 설정하고, 주어진 순서의 선행 인수가 있는 새로운 함수를 생성
var m = {
x: 'B',
get: function(val) { return val + "," + this.x; }
}
console.log(m.get()); // undefined,B
console.log(m.get('A')); // A,B
var get1 = m.get;
console.log(get1()); // undefined,undefined
var get2 = get1.bind(m);
console.log(get2()); // undefined,B
var get3 = get1.bind(m, 'A');
console.log(get3()); // A,B
| IE8 | IE9 | IE10 | IE11 | chrome | firefox | safari |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
JSON
JSON is a syntax for serializing objects, arrays, numbers, strings, booleans, and null. some JavaScript is not JSON, and some JSON is not JavaScript. See also JSON
| JavaScript | JSON differences |
|---|---|
| Objects and Arrays | 속성(property)명은 큰따옴표로 묶여야 한다; 후행(trailing) 쉼표는 금지. |
| Numbers | 선행(leading) 0은 금지됩니다; 소수점은 적어도 한 자릿수가 뒤따라야 합니다. |
| Strings | 문자열은 큰따옴표로 묶여야 합니다 |
| IE8 | IE9 | IE10 | IE11 | chrome | firefox | safari |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Immutable globals
undefined NaN Infinity
var undefined = "a";
console.log(undefined); // undefined
var NaN = 24;
console.log(NaN); // NaN
var Infinity = 21;
console.log(Infinity); // Infinity
| IE8 | IE9 | IE10 | IE11 | chrome | firefox | safari |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Function.prototype.apply permits array-likes
function func(a,b) {
console.log(a + ", " + b);
}
console.log(func.apply({}, [1,2])); // 1, 2
console.log(func.apply({}, {0:1, 1:2, length:2})); // 1, 2
console.log(func.apply({}, {0:1, 1:2})); // undefined, undefined
| IE8 | IE9 | IE10 | IE11 | chrome | firefox | safari |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
parseInt ignores leading zeros
console.log(parseInt('10') === 10); // true
console.log(parseInt('010') === 10); // true
| IE8 | IE9 | IE10 | IE11 | chrome | firefox | safari |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Function “prototype” property is non-enumerable
function func() {}
console.log(func.propertyIsEnumerable('prototype'));
| IE8 | IE9 | IE10 | IE11 | chrome | firefox | safari |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Arguments toString is “Arguments”
function func(){
console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call(arguments));
// [object Arguments]
}
func();
| IE8 | IE9 | IE10 | IE11 | chrome | firefox | safari |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Zero-width chars in identifiers
var _\u200c\u200d = true;
console.log(_\u200c\u200d); // true
console.log("[\u200c\u200d]") // []
| IE8 | IE9 | IE10 | IE11 | chrome | firefox | safari |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Unreserved words
abstract, boolean, byte, char, double, final, float, goto, int, long, native, short, synchronized, transient, volatile
var int = true;
console.log(int); // true
| IE8 | IE9 | IE10 | IE11 | chrome | firefox | safari |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Thrown functions have proper this values
function func() {
try {
throw function(obj) {
console.log(this.a + "," + obj.a);
};
} catch(e) {
var _this = this;
this.a = 'a';
e(_this);
}
}
func.apply({}); // undefined,a
| IE8 | IE9 | IE10 | IE11 | chrome | firefox | safari |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Reference
ECMAScript compatibility table - http://kangax.github.io/compat-table/es5/